The authenticity of meals is of accelerating significance for producers, retailers and customers. All teams profit from the proper labelling of the contents of meals merchandise. Producers and retailers need to assure the origin of their merchandise and examine for adulteration with cheaper or inferior substances.
Customers are additionally extra demanding in regards to the origin of their meals for numerous socioeconomic causes. In distinction to this rising demand, right labelling has change into rather more complicated due to international transportation networks of uncooked supplies and processed meals merchandise.
Inside the European built-in analysis venture ‘Tracing the origin of meals’ (TRACE), a DNA-based multiplex detection instrument was developed-the padlock probe ligation and microarray detection (PPLMD) instrument.
On this paper, this methodology is prolonged to a 15-plex traceability instrument with a concentrate on merchandise of business significance such because the emmer wheat Farro della Garfagnana (FdG) and Basmati rice.
The specificity of 14 plant-related padlock probes was decided and initially validated in mixtures comprising seven or 9 plant species/varieties. One nucleotide distinction in goal sequence was adequate for the excellence between the presence or absence of a particular goal.
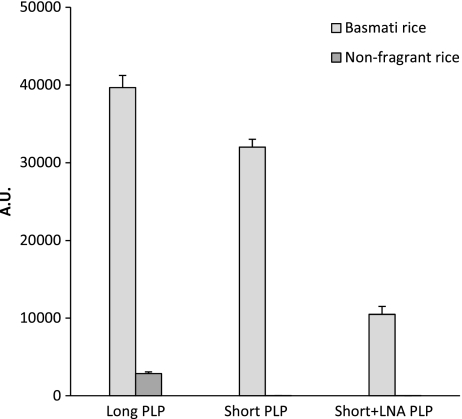
Not less than 5% FdG or Basmati rice was detected in mixtures with cheaper bread wheat or non-fragrant rice, respectively. The outcomes instructed that even decrease ranges of (un-)intentional adulteration could possibly be detected.
PPLMD has been proven to be a great tool for the detection of fraudulent/intentional admixtures in premium meals and is prepared for the monitoring of right labelling of premium meals worldwide.
Comparability of strategies for correct quantification of DNA mass focus with traceability to the worldwide system of items.
Correct estimation of complete DNA focus (mass focus, e.g., ng/muL) that’s traceable to the Worldwide System of Models (SI) is an important place to begin for bettering reproducible measurements in lots of purposes involving nucleic acid testing and requires a DNA reference materials which has been licensed for its complete DNA focus.
On this examine, the concentrations of six totally different lambda DNA preparations had been decided utilizing totally different measurement platforms: UV Absorbance at 260 nm (A(260)) with and with out prior sodium hydroxide (NaOH) therapy of the DNA, PicoGreen assay, and digital polymerase chain response (dPCR).
DNA focus estimates by A(260) with and with out prior NaOH therapy had been considerably totally different for 5 of the six samples examined. There have been no vital variations in focus estimates based mostly on A(260) with prior NaOH therapy, PicoGreen evaluation, and dPCR for 2 of the three samples examined utilizing dPCR.
Because the measurand in dPCR is quantity (copy quantity) focus (copies/muL), the outcomes recommend that correct estimation of DNA mass focus based mostly on copy quantity focus is achievable offered the DNA is totally characterised and within the double-stranded kind or amplification is designed to be initiated from solely one of many two complementary strands.
